Content
Vitamins K are a group of fat-soluble substances that are involved in protein synthesis and blood clotting. They are divided into 2 types: phylloquinone (K1) and menaquinone (K2). Vitamin K1 is needed by the body to synthesize bone protein and stop bleeding. But it has other functions as well.
What is vitamin K1 for?
The main purpose of phylloquinone is to maintain normal blood clotting levels. Vitamin K1 is involved in the production of substances that are needed to stop bleeding. He begins to work in the tissues of the liver. It activates the synthesis of special cells in the liver that are responsible for blood clotting.
Phylloquinone participates in the production of osteocalcin - protein molecules of bone tissue. Vitamin K1 helps to properly absorb calcium and vitamin D, is responsible for the restoration and formation of bones, and prevents the development of osteoporosis in women during menopause. It also has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the kidneys, reducing the risk of stones formation in them.
What vitamin K1 contains
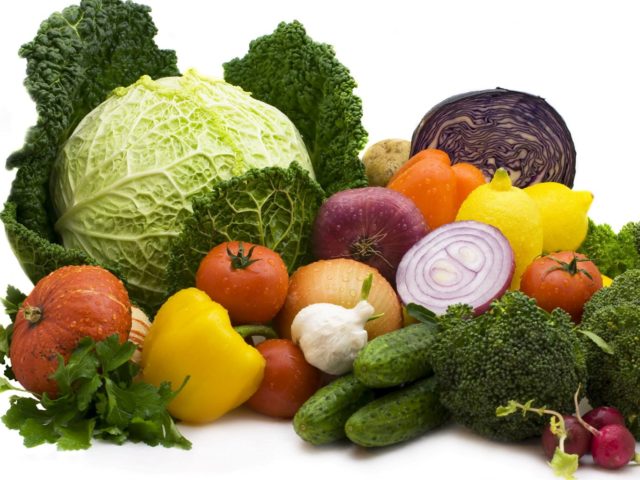
Vitamin K1 - phylloquinone, found in plants. Spinach and other leafy vegetables, greens are rich in this substance:
- nettle;
- parsley;
- soy;
- lettuce;
- white cabbage, Brussels sprouts and cauliflower;
- broccoli.
K1 is also contained in other products: cereals, wheat bran, avocado, pumpkin, kiwi, bananas, avocado, black currant, carrot. These products should be emphasized in patients who are suspected of having a vitamin K1 deficiency in the body.

Vitamin K1 norm
K1 dosage is selected individually. It depends on the weight and age of the patient:
- babies - 2.0-2.5 mg;
- children 1-3 years old - 30 mg;
- children 4-9 years old - 55 mg;
- children 10-13 years old - 60 mg;
- adolescents - 75 mg;
- adults - 90-120 mg.
With a balanced diet rich in vegetables, you can get the full amount of vitamin K1 you need from food. For patients with few vegetables on the menu, doctors recommend taking fortified supplements. The same should be done by people who sit on mono-diets or take medications that block the absorption of phylloquinone.
Deficiency and excess of vitamin K1
Before you start taking vitamin K1, you need to figure out how its excess and deficiency affects the body.
With a deficiency of vitamin K1 in the body, even with a small cut, it will be difficult to stop the blood. No less dangerous is the likelihood of internal hemorrhages or other disorders of blood coagulation. Problems can arise during surgery.
Women can notice a deficiency of this vitamin during menstruation. If it is not enough, then menstruation will be long and abundant. Patients suffering from phylloquinone deficiency complain of frequent nosebleeds, bleeding from hemorrhoids (with hemorrhoids), and frequent intestinal disorders.
Calcium cannot be absorbed without vitamin K1. When it enters the body, it is not distributed in the bones, but is released naturally in the urine. Phylloquinol deficiency affects the absorption of vitamin D. With a deficiency of this substance, the work of the circulatory system is disrupted: calcium accumulates around the vessels. Due to calcification, the arteries become hard and their elasticity deteriorates.
You can suspect a lack of K1 in the body if:
- bleeding does not stop well even with minor cuts;
- wounds, bruises, abrasions take longer to heal;
- the work of the digestive system is disrupted, which manifests itself in the form of intestinal disorders;
- the mobility of the joints has worsened (they ossify).
An indirect sign of deficiency is increased sleepiness and fatigue. Deformation of developing bones is possible.
When eating foods that are rich in K1, the risk of hypervitaminosis is minimal. But when you take synthetic vitamins, there is a possibility of their accumulation in the body in excess. An excess leads to an increase in the number of platelets, an increase in blood viscosity. As a result, a person may begin to form blood clots in their blood vessels.
Vitamin K1 supplementation
In case of an unbalanced diet or suspected K1 deficiency in the body, it is recommended to start taking the appropriate vitamins. The source of vitamin K1 can be Fitomenadion. In people with a deficiency of this substance in the body, oral administration, injection or drip administration of the drug normalizes metabolism and increases blood clotting.
It is recommended for patients who have been diagnosed with hemorrhagic syndrome (deterioration of the blood coagulation process) caused by vitamin K1 deficiency. The intake of vitamin-containing preparations is indicated for patients who have a disturbed process of its absorption from food. This is possible if the patient has:
- obstructive jaundice;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- ulcerative colitis;
- hepatitis;
- cystic fibrosis of the pancreas;
- tropical sprue;
- gluten intolerance;
- enteritis;
- cystic fibrosis;
- chronic diarrhea.
Fitomenadion is recommended as a source of vitamin K for patients after an overdose:
- indirect anticoagulants of the indandione and coumarin series;
- sulfonamides;
- salicylates;
- broad-spectrum antibiotics;
- tranquilizers.
The use of synthetic vitamin K1 is indicated for prophylactic purposes before planned operations and for hemorrhagic diseases in newborns.
In case of K1 deficiency, it is not necessary to use Fitomenadion, it can be replaced with analogs. Depending on the patient's condition, the doctor may recommend Konakion or multivitamin complexes.
The drug can be administered to newborns with hemorrhages of any form. Treatment should be started prior to diagnosis. It is important to reduce the manifestations of the disease, and the cause of its occurrence can be identified after the first symptoms are eliminated. Long-term diagnostics can be fatal.
When taken orally, the drug begins to be absorbed in the small intestine if there is bile in it. Only after that does it enter the lymph and blood. With intramuscular and intravenous administration, the effect appears faster. After oral administration, the action begins only after 6-10 hours, and after intramuscular administration - within 1 hour.
Precautions
When taking synthetic drugs that saturate the body with K1, there is a risk of overdose.Therefore, it is important to use it in the doses indicated in the instructions or prescribed by your doctor.
Fitomenadion blocks the action of indirect coagulants, so they are not prescribed at the same time. Before starting the administration of drugs that increase blood clotting, it is necessary to check the indicators of hemocoagulation:
- platelet count;
- heparin tolerance;
- prothrombin index.
They must be monitored throughout the entire treatment period.
If Fitomenadion is used as a source of K1, then it is important to follow the rules for its administration. It can be taken orally or injected intramuscularly, intravenously, subcutaneously.
Oral administration is not recommended if the formation or excretion of bile is impaired. When administered intravenously, it is important to monitor the speed, only slow infusions are allowed. The rate of administration of Fitomenadione should not exceed 1 mg / min, otherwise the likelihood of severe allergic reactions, up to the development of anaphylactic shock, increases.
Contraindications and side effects
Taking funds, sources of vitamin K1 for the body, is prohibited for patients who have:
- rapid blood clotting;
- tendency to thrombus formation;
- individual intolerance to the substances that make up the drugs;
- a history of thromboembolism.
Caution should be observed by people suffering from varicose veins. Without a doctor's prescription, synthetic sources of K1 are not recommended for pregnant women, nursing mothers and children.
While taking it, there is a risk of side effects. Among the most common complications are:
- redness of the skin;
- feeling hot;
- short-term lowering of blood pressure;
- dyspnea;
- tachycardia;
- weakness;
- taste disturbances;
- profuse sweating;
- local allergic reactions in the form of a skin rash;
- common allergic reactions - anaphylactic or anaphylactoid shock.
With parenteral routes of administration, pain and swelling may occur at the injection site. With repeated administration, patients may experience skin changes characteristic of scleroderma, the formation of an infiltrate, and itching of the skin. A side effect in children is hyperbilirubinemia.

Conclusion
Vitamin K1 is needed by the body to normalize the work of the blood coagulation system, maintain the health of bones, joints, blood vessels. People who eat well and do not suffer from diseases associated with impaired absorption of K1 in the body do not face a deficiency of this vitamin. But with increased bleeding, it is advisable to be examined and, if indicated, start taking special medications.

