Content
The largest class of plant polyphenols are flavonoids. They are a secondary metabolite of higher plants and represent a large class of phenolic compounds found in fruits, vegetables, herbs, cocoa and some drinks. Used in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and biological additives. Produced in the form of a fortified product. The flavonoid complex has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimutagenic and anticarcinogenic properties, combined with their ability to modulate the function of key cellular enzymes.
What are flavonoids
Polyphenol compounds are an important class of natural products, in particular, they are classified as secondary plant metabolites with a polyphenolic structure. Flavonoids are hydroxy derivatives of flavones and have different biochemical and antioxidant effects related to diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer's disease, atherosclerosis, etc.
Plant polyphenol compounds are associated with a wide range of health-promoting effects and are indispensable in the nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, medicinal and cosmetic industries. Flavonoids are known to be potent inhibitors of a number of enzymes, such as xanthine oxidase, cyclooxygenase, lipoxygenase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase.
They belong to the class of low molecular weight phenolic compounds that are widespread in the plant kingdom.
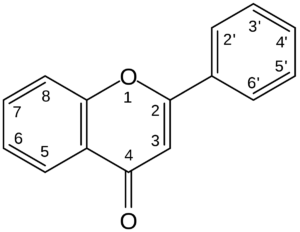
Types of flavonoids
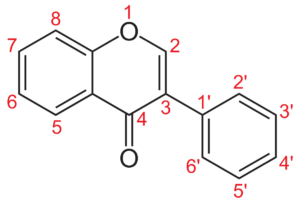
Polyphenols are naturally occurring substances with three hydroxyl groups. Flavonoids are classified into subgroups depending on the number of carbon atoms in ring C to which ring B is attached, as well as the degree of unsaturation and oxidation of ring C.
Flavones are one of the important subgroups of polyphenols. These substances in leaves, flowers and fruits in the form of glucosides. Celery, parsley, red peppers, chamomile, mint and ginkgo biloba have become some of the main sources of this form of plant polyphenols.
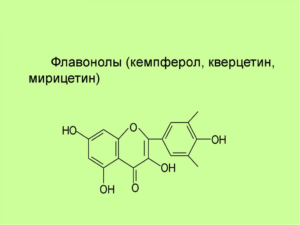
Flavonols are the building blocks of proanthocyanins. The substance is found in abundance in various fruits and vegetables. Onions, cabbage, lettuce, tomatoes, apples, grapes and berries are rich in this compound. Plant polyphenol has a hydroxyl group at the 3-position of the C-ring, which can also be glycosylated.
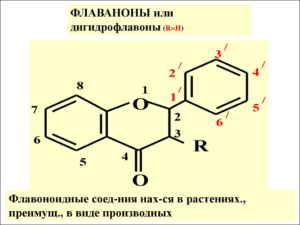
Flavanones, also called dihydroflavones or catechins, are 3-hydroxy derivatives. Bananas, apples, blueberries, peaches and pears are abundant.
Flavanones are found in all citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, and grapes. Polyphenol compounds are responsible for the bitter taste of the juice and the peel of the Rutov family. Citrus flavonoids have a pharmacological effect as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, hypolipidemic and hypocholesterolemic agents.
Isoflavonoids have only limited distribution in the plant kingdom and are found mainly in soybeans and other legumes. Polyphenol compounds have tremendous potential in the fight against a number of diseases.
Neoflavonoids are a class of polyphenolic substances. Found in the seed of Calophyllum inophyllum.
Plant polyphenol compounds called chalcones are characterized by the absence of a C ring. They can be called open chain flavonoids. The substances are found in tomatoes, pears, strawberries, bearberry, and some wheat products. Chalcones and their derivatives have attracted attention for their numerous nutritional and biological benefits.
Flavonoids and their derivatives are presented in the table.
|
Name of connections |
Examples of substances |
|
Anthocyanins |
Lelargonidin, cyanidin, delphinidin, peonidin, petunidin. |
|
Flavonols |
Luteolin, Apigenin and Tangeritin. |
|
Flavanones |
Naringenin, naringin, hesperitin, eriodicitol |
|
Flavones |
Sinensetin, isosinensetin, nobiletin, luteolin, tangeretin. |
|
Isoflavones |
Genistein, daidzin, daidzein. |
|
Hulkons |
Floridzin, arbutin, phloretin and chalconaringenin |
What does the body need flavonoids for?
Human health directly depends on what trace elements enter the body with food. The lack of any of them can cause serious consequences in the disruption of the work of any of the internal organs. The use of plant polyphenols has a positive effect on the body of men and women.
The effect of flavonoids on a woman's body
Women should consume foods rich in plant polyphenols during the postmenopausal period. According to a number of scientists, the regular use of these compounds, especially catechins, leads to a decrease in the risk of death from coronary disease.
Women's health depends on flavonoids in pre- and postmenopausal women. These polyphenol compounds reduce plasma lipids and reduce the severity of oxidative stress. Taking decoctions and infusions from medicinal plants containing flavonoids has a cardioprotective effect.
Pregnant women are advised to abandon these plant compounds, choose more benign products without plant polyphenols. Preparations containing flavonoids have a negative effect on nursing mothers.
The effect of flavonoids on the male body
These compounds can prevent the development of prostate cancer. The beneficial properties of flavonoids for men were confirmed by a study in which 1,500 patients took part.
The risk of developing severe prostate cancer is reduced by 30% with regular consumption of foods containing polyphenol compounds.
The mechanism of action of flavonoids
The antioxidant activity of organic compounds depends on their functional hydroxyl groups, which can mediate antioxidant effects by scavenging free radicals and chelating metal ions. The mechanisms of action of substances include the suppression of the formation of reactive oxygen species by inhibiting enzymes, chelation of trace elements involved in the formation of free radicals, ROS uptake, and regulation or antioxidant defense.
Flavonoids exhibit anti-inflammatory effects, which can be mediated by inhibition of both activity and production of various pro-inflammatory substances. Plant polyphenols also produce tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase.
The action of flavonoids is multifaceted and depends on parallel processes. Among the main mechanisms of organic compounds of polyphenols:
- antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity;
- regulation of blood pressure;
- lowering cholesterol levels;
- protection of LDL from oxidative modification;
- antiplatelet action.
Flavonoids protect lipids from oxidative damage by various mechanisms. Due to their antioxidant and chelating properties, organic compounds of plant polyphenols inactivate reactive oxygen species, thus counteracting the oxidation of LDL in plasma. In addition, the compounds facilitate inflammation of the endothelium of blood vessels.
The antiarteriosclerotic effect of flavonoids is associated with a decrease in inflammation in the blood vessel wall by inhibiting leukocyte influx. Several compounds exhibit antiplatelet aggregation effects through various mechanisms, including inhibition of the arachidonic acid pathway. Substances reduce the activity of enzymes involved in the formation of prostaglandin leukotrienes and thromboxane A2 from arachidonic acid.
Anthocyanins lower blood cholesterol levels in patients at high risk for cardiovascular disease. In a 6-month study of flavonoids, the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) was reduced after anthocyanins (320 mg / day) in 122 patients with hypercholesterolemia.
Catechins play a role in improving risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Substances regulate the amount of ribonucleic acid. These compounds are able to influence the activity of metabolic enzymes that improve oxidation and block fatty acid synthesis.
This specific action of catechins leads to a decrease in lipid levels in the blood and liver. The plant compound reduces the deposition of fat in the body, thereby reducing the early onset of cardiovascular disease in children.
Flavonoids are able to influence β-cell mass and function, as well as energy metabolism and insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues. Plant polyphenol compounds increase glucose uptake through translocation of GLUT4 vesicles to the cell membrane.
Flavonoids can enhance glucose uptake in response to insulin by stimulating adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase and other kinases such as ERK1 / 2 and P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38MAPK).
Substances have a spectrum of biological activity. At the stages of initiation and promotion, polyphenol compounds include: inactivation of carcinogens, inhibition of cell proliferation, enhancement of DNA repair processes and a decrease in oxidative stress. In the progression phase, flavonoids induce apoptosis, inhibit angiogenesis, exhibit antioxidant activity, and also trigger a cytotoxic or cytostatic effect against cancer cells.
The action of bioflavonoids is aimed at improving the absorption of vitamin C from the intestinal lumen, preventing its destruction under the influence of oxidants. They have roughly the same effect. Therefore, scientists have combined them into a large group, all bioflavonoids are "vitamin P".

Bioflavonoids strengthen the capillary walls, protect and restore the liver after taking high doses of alcohol and drugs. Vitamin stabilizes cell membranes, exhibiting antiallergic effect.
The benefits and harms of flavonoids
The positive effect of flavonoids on the body has been proven by numerous studies. Benefit:
- compounds of the largest class of flavonoids normalize the immune system;
- regulate the degree of permeability of the vessel walls;
- inhibit the production of serotonin and histamine;
- plant polyphenols rejuvenate the body;
- protect against infectious diseases;
- substances inhibit the growth of tumor cells.
Flavonoids have a positive effect on the liver. The compounds are involved in the formation of bile and regulate the rate of urine production.
Negative properties of flavonoids and contraindications:
- large doses inhibit the absorption of vitamins;
- negatively affect the functioning of the thyroid gland;
- should not be taken with poor blood clotting;
- to avoid side effects, the recommended dosages of plant polyphenols should not be exceeded.
What foods contain flavonoids
Important food sources of compounds of the plant polyphenol class are vegetables, fruits, seeds and some grains, as well as wine, tea and spices. The most common sources of these substances are berries, peas, cabbage, dark chocolate, parsley, oregano, capres, green and black tea.
The content of plant polyphenols in food (mg / 100 g) is presented in the table:
|
Flavonoid content range mg / 100 g |
Products (amount of substances mg / 100 g) |
|
> 1500 |
Dried parsley (4854.49), oregano, Mexican, dried (1545.79). |
|
300–1500 |
Elderberry (518.13), raw caprice (493.03), chokeberry (368.66) |
|
100–300 |
Peas (277.41), fresh parsley (233.16), black currant (167.47), blueberry (158.51), blackberry (137.66), brewed green tea (121.27), black tea (119.32), cranberry (113.58), dark chocolate (108.60), cocoa (106.68). |
|
70–100 |
Cabbage (92.98), dill (84.50), red currant (79.49), kumquats (79.26), black currant juice (78.04), white tea (74.60). |
|
40–70 mg |
Arugula (69.27), red cabbage (64.34), peppermint (60.48), grapefruit (55.40), lemons (53.38), oolong tea (52.37), lime (48.60 ), red grapes (48.35), fresh thyme (47.75). |
|
10–40 |
Strawberries (34.31), pecans (34.01), beans (28.00), radishes (26.52), wheat (25.85), orange juice (24.13), green celery (22.60) , artichokes (22.20), green onions (21.67), pear (21.53), chili (21.17), beans (20.63). |
|
<10 |
Boiled Brussels sprouts (7.68), green peppers (6.98), beer (3.34). |
The use of plant flavonoids
Flavonoids enhance the action of many medicinal substances. They were used in medicine, cosmetology and the production of cosmetics.
Flavonoids in medicine
In pharmacology, compounds of plant polyphenols are used for edema of renal and cardiac origin. The substances are effective for urolithiasis, biliary dyskinesia and hepatitis.
The class of plant polyphenols is used for uterine, hemorrhoidal and nosebleeds. Chemical compounds for the manufacture of medicines and the treatment of these problems are obtained from the herb of Knotweed and Kidney.
The class of plant polyphenols is widely used in children's practice. The compounds are used as an antiallergic agent for diasthesis. For children, the substance is prescribed in the form of an infusion for internal use, baths and lotions from medicinal plants are used externally.
Polyphenol compounds are used as an expectorant, antitumor.
Flavonoids in cosmetology
Plant substances prevent intense keratinization by reducing enzymatic activity. These compounds dilate blood vessels, stimulating microcirculation. They have a rejuvenating effect.
The most valuable extracts rich in plant polyphenols:
- grape seeds;
- ginseng;
- green tea;
- kella extract.

Flavonoids in cosmetics prevent lipid oxidation and inhibit the activity of enzymes - elastase, collagenase and hyaluronidase.
Conclusion
The flavonoid complex is widely used in cosmetics and medicine due to its low toxicity and diverse action. New methods of compound purification, stabilization and delivery are continuously being developed. Such methods make it possible to include substances in anti-aging agents in an increased amount.

